Research
A gallary of research projects
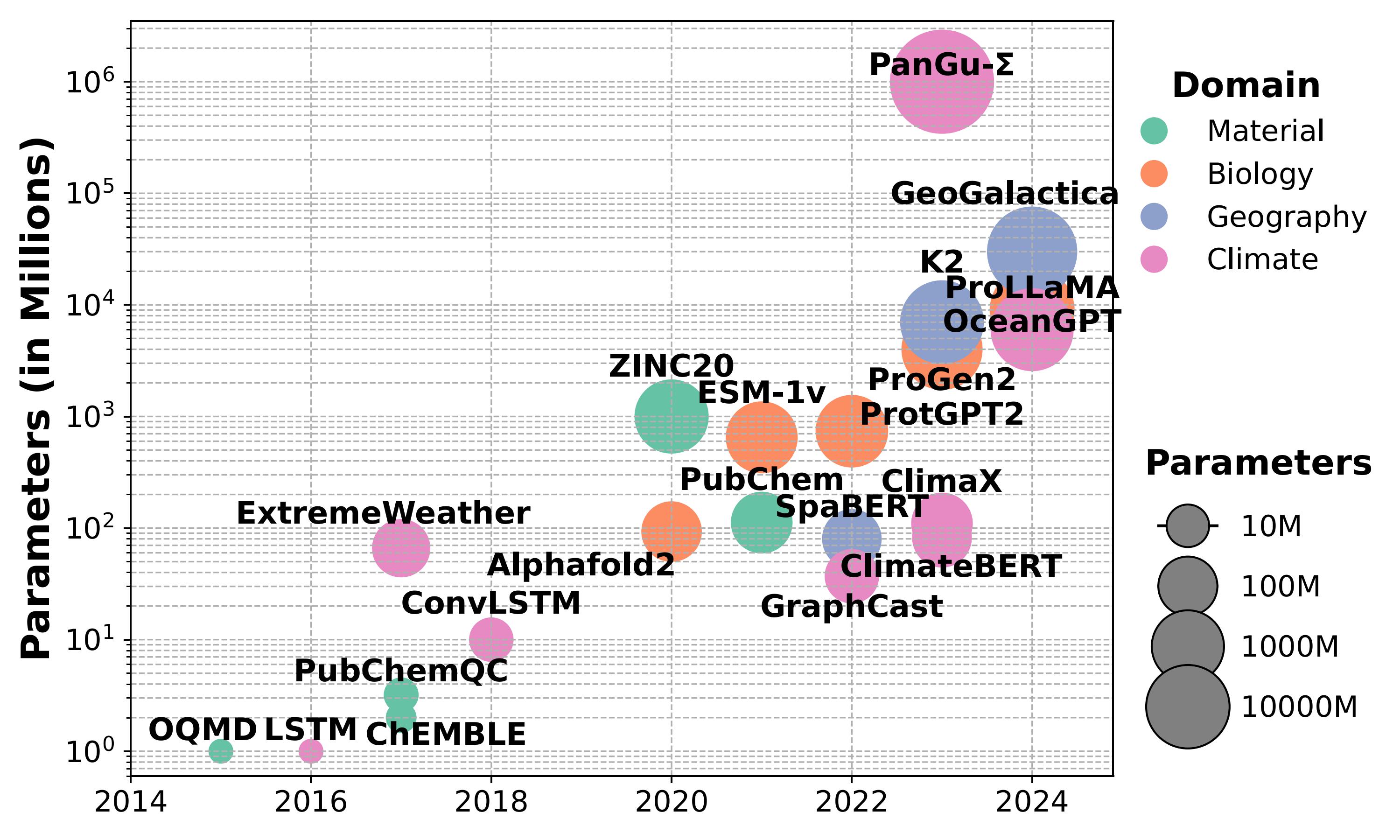
Exploring Next-Generation AI for Scientific Discovery
SciML is undergoing a paradigm shift with the advent of foundation models like AlphaFold-3, PanGu-Σ, and ClimaX, which are trained on extensive datasets using large-scale self-supervision and can be adapted to various downstream tasks. These general-purpose subject matter experts (SMEs) demonstrate superior accuracy compared to traditional specialized DNN models. For example, the new AlphaFold3 model demonstrates substantially higher performance in all but one category compared to previous DNN methods specializing in specific tasks. This paradigm shift is also being undertaken in other domains, such as Prithvi and GraphCast in climate science; DeepMind's GNN and ESM-1b in biology; Planck, WMAP, and Euclid in cosmology; and ChemBERTa, MatBERT, and ANI-1 in chemistry.
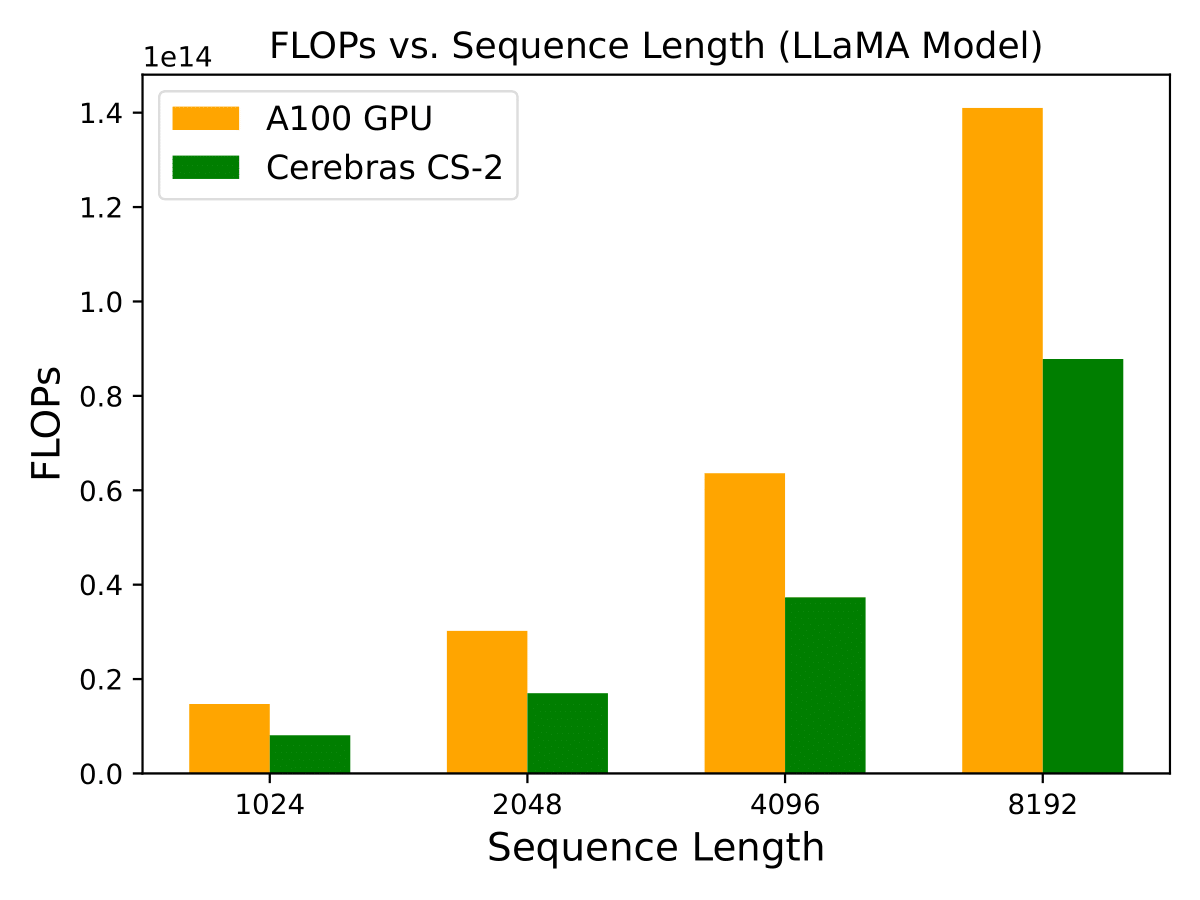
Accelerating Large-Scale AI Models on AI Accelerators
The acceleration of large-scale AI models is undergoing a paradigm shift with the rise of specialized hardware such as NVIDIA GPUs, Google TPUs, Cerebras wafer-scale processors, and FPGA-based systems. These accelerators are tailored to the computational needs of LLMs, GNNs, and CNNs, enabling massive parallelism, high-bandwidth memory access, and optimized data movement. Cerebras eliminates inter-chip communication bottlenecks with wafer-scale integration, achieving training throughput that was previously unattainable.
System Optimization for Large Scale AI Models
Large-scale AI models such as LLMs, GNNs, and CNNs are driving a fundamental shift in how systems are designed and optimized. As these models grow to billions of parameters and are trained on increasingly massive datasets, traditional training pipelines become insufficient. Meeting these demands requires advances in distributed training strategies, hardware-aware scheduling, and scalable parallelization. Techniques like mixed-precision computation, pipeline parallelism, and memory-efficient execution are now central to achieving state-of-the-art performance while controlling cost and energy use.